Botbusters
Zasoby marketingowe
Scammer traffic providers utilize bots to mislead website owners. Let's try to understand why this happens, why bots are dangerous for businesses and how to track them.
How it happens
The fraud scheme is usually simple. For example, the Brown & Sons furniture company launches a new sofa. Mr Brown, the company's CEO, decides to have a big sale on their site in an attempt to attract new clients and to generate more profits. The company places an advert on the home page and purchases traffic aiming to show the offer to 100,000 people.
Website traffic has increased, but sales are not growing. The traffic seller suggests that the offer is not attractive enough. Mr Brown takes new photos, while his sons write more attractive sofa descriptions. Once the updated offer is ready, the company purchases more traffic. The result is not much improved and falls within the statistical error.
Mr Brown and his sons start to suspect there might be something wrong with the traffic, but the seller provides reports with tables and
diagrams. Nothing is clear, except that the seller has provided even more traffic than the company requested. Then, Brown & Sons make
one last desperate attempt: they revise the registration form and add the "Order a callback" button. However, the newly purchased traffic
package leads to the same outcome. High website traffic still exists but the desired outcome is not generated. The conversion rates are
growing, but sofa sales do not.
Conclusion: Brown & Sons spent a lot of money and effort. In return, the company remained strategically stagnant, without being able to apply successfully their operational visions, indicating an inability of the advertising to deliver.
Failure reasoning
The situation could be avoided if Mr Brown had analyzed the purchased traffic after the first campaign. He would have concluded that the traffic was created by simple bots visiting the desired pages. The fraudulent seller artificially inflated traffic to manipulate the efficiency statistics.
In the above example, bots visited the desired pages to imitate advert views. More advanced bots can produce button clicks if the traffic is
purchased on the pay-per-click basis. Furthermore, fraudulent sellers can utilize highly sophisticated technologies to imitate any
human actions. In this case, the customer will never guess that the traffic is fake.
In large high-traffic sites, where each bot cannot be traced manually, a technologically advanced solution may come in handy.
How Finteza tracks bots
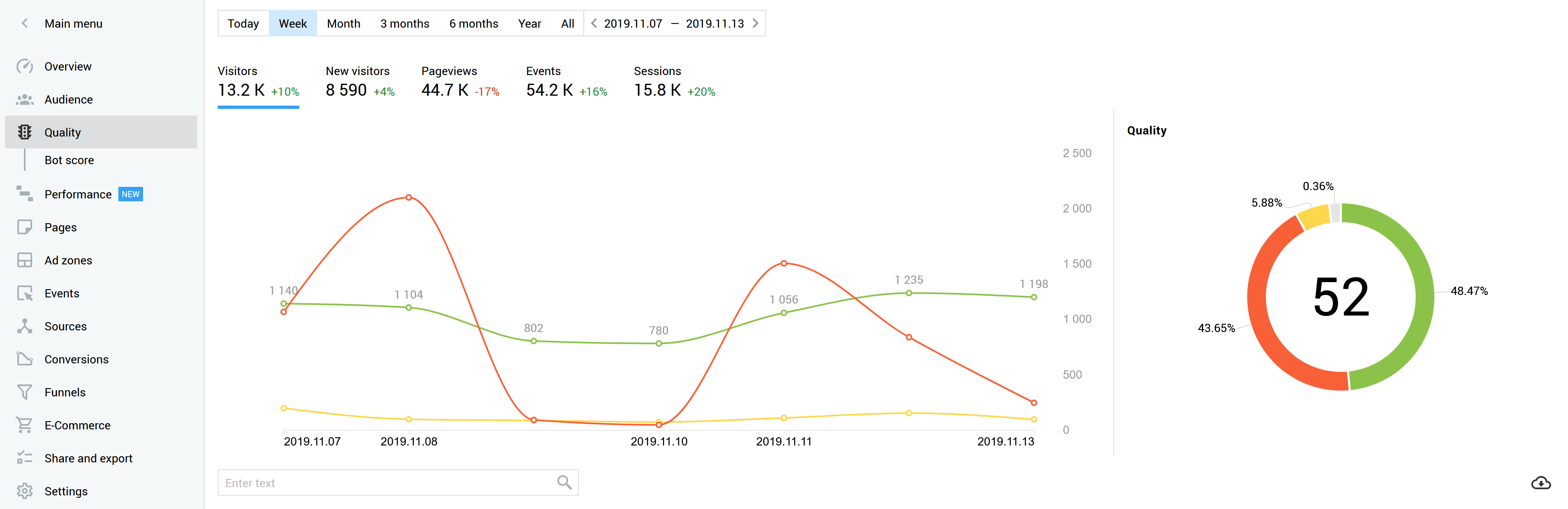
In the first stage, technical parameters of visits are evaluated, and 12 types of bad traffic are identified according to formal metrics (through the analysis of operating systems, browsers, IP addresses, screen resolution and others). Assessment results appear under the Quality section.
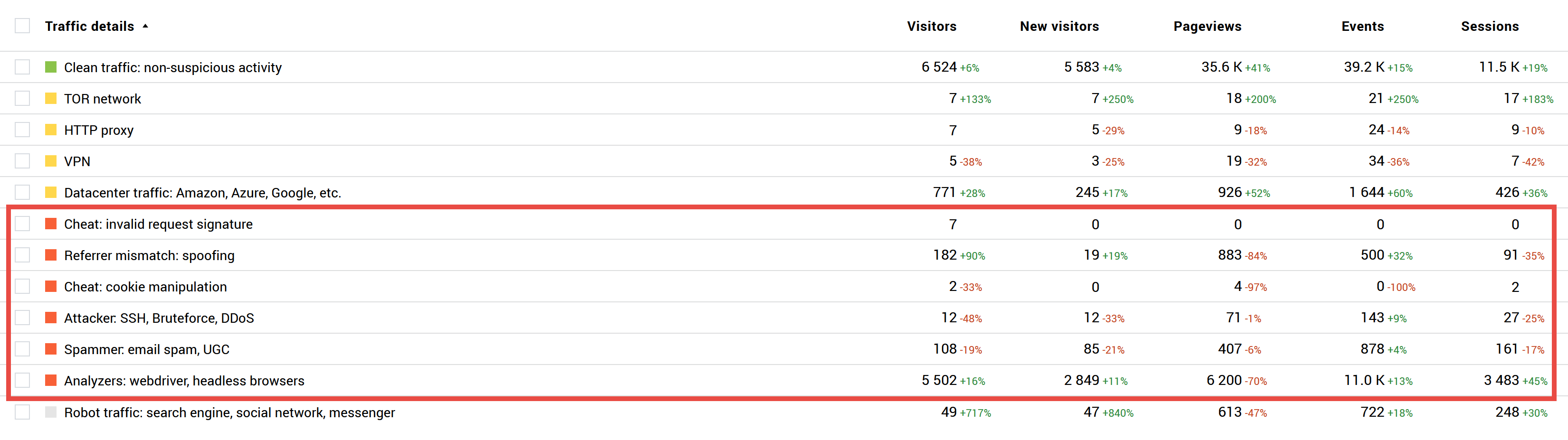
The section shows which group the bots belong to: spam sending, password guessing or malignant actions imitation. Brown & Sons should pay attention to the "Referrer mismatch: spoofing" section. This section includes the traffic which tries to fake its source. The company requested advertising in interior design websites. Reports show that traffic originates from exactly these websites. Unfortunately, the source of visits which originate from different sites can be easily spoofed in reports. This is the most obvious indication of manipulated traffic. Another group called Analyzers shows visits from headless browsers. Such browsers cannot be utilized by humans, but they are often used by traffic-inflating bots.
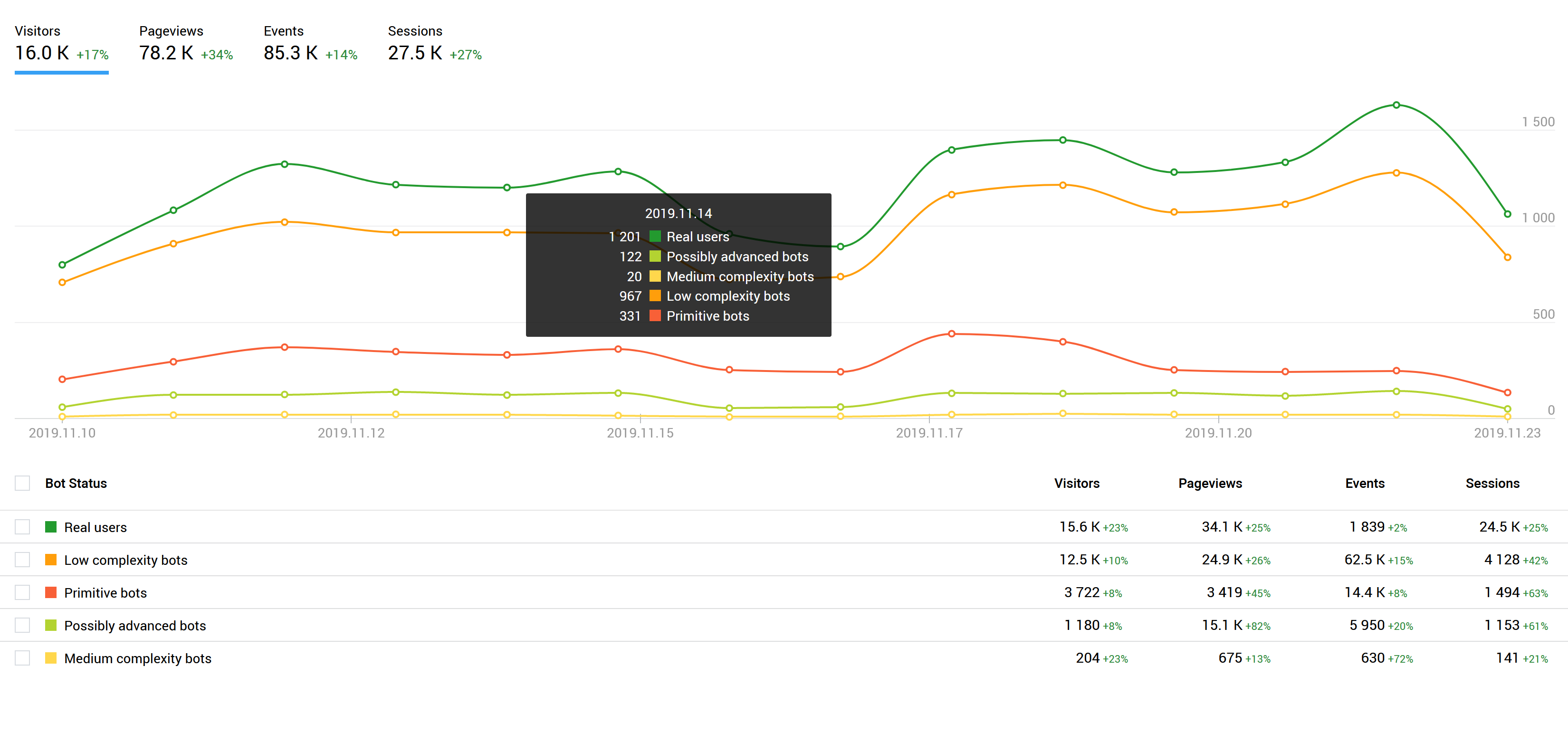
In the second stage, the visitor behavior is analyzed, in an attempt to determine whether the user is a human or a bot. If it is a bot, its complexity is further evaluated. Advanced bots and simple scripts can be utilized for the same purpose. For example, they can inflate video views or imitate banner clicks. It is even more challenging to spot such highly sophisticated bots. The overall picture of bot traffic is shown under the Bot Score section.
How it works
Each visitor is checked and identified by a whole set of variables. Let us view an example of such variables:
- Imitation of mouse movements or screen touches
- Hardware used by the visitor
- The time between user actions
And a few dozen of other statistics. If any discrepancy is detected, the visitor is given penalty points. The number of points depends on the violation severity. The maximum number of points can be assigned for the most severe violations. In this case, the traffic is instantly moved to the red category. The points add up to the overall rating which is shown in Finteza.
Finteza divides traffic into five categories:
- Red: simple bots that do not really try to hide.
- Orange: low-complexity bots which cannot be spotted manually.
- Yellow: complex bots that may perform human-like actions. Finteza can efficiently trace such bots even though distinguishing them from human visitors is a challenging task.
- Light green: sophisticated bots which can mimic human behavior convincingly. They can only be identified based on a complex analysis of page views, origins, behavior and other variables. Such a trophy can be proudly hung over the fireplace after a hunt.
- Dark green: real users. No hunting is allowed in this category.
A decrease in dark green traffic alongside an increase in other traffic types may indicate bot issues which can cause your business to lose money. The sooner you correct these issues the better, while the cost of inaction can be dramatic. This is the reason why we deliver data in real time, enabling instant response to extreme situations.
What's next?
High-quality analytics can assist in protecting businesses from scammers, in avoiding extra costs and in controlling bot visits. With Finteza, you
can detect bots in real time, identify traffic sources and determine bot targets. With all these statistical information in hand, you can
efficiently respond to traffic issues in a timely manner.
Add the Finteza code into your site for free and start hunting bots.